What issue can we solve for you?
Type in your prompt above or try one of these suggestions
Suggested Prompt



What is Generative AI: From Now to Next
Generative AI is an overnight sensation,
70 years in the making.
There are many things in our lives that have been called “artificial intelligence.” From Microsoft’s Clippy to Apple’s Siri to Amazon’s Alexa to facial recognition to unlock your smartphone—all of these innovations were once considered ground-breaking artificial intelligence applications that today we would just call technology.
What is generative AI: It’s all about the data
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that is capable of creating new content, such as images, videos or text, without being explicitly programmed to do so. It works by analyzing and learning from large datasets of examples and then uses this knowledge to generate new content that is similar to the original examples.
For example, a generative AI system could be trained on a dataset of images of animals and then be asked to generate new images of animals. It would use its understanding of the patterns and structures of animal images to create new, unique images that are similar to those in the original dataset.
How was generative AI created: A clever chess gambit
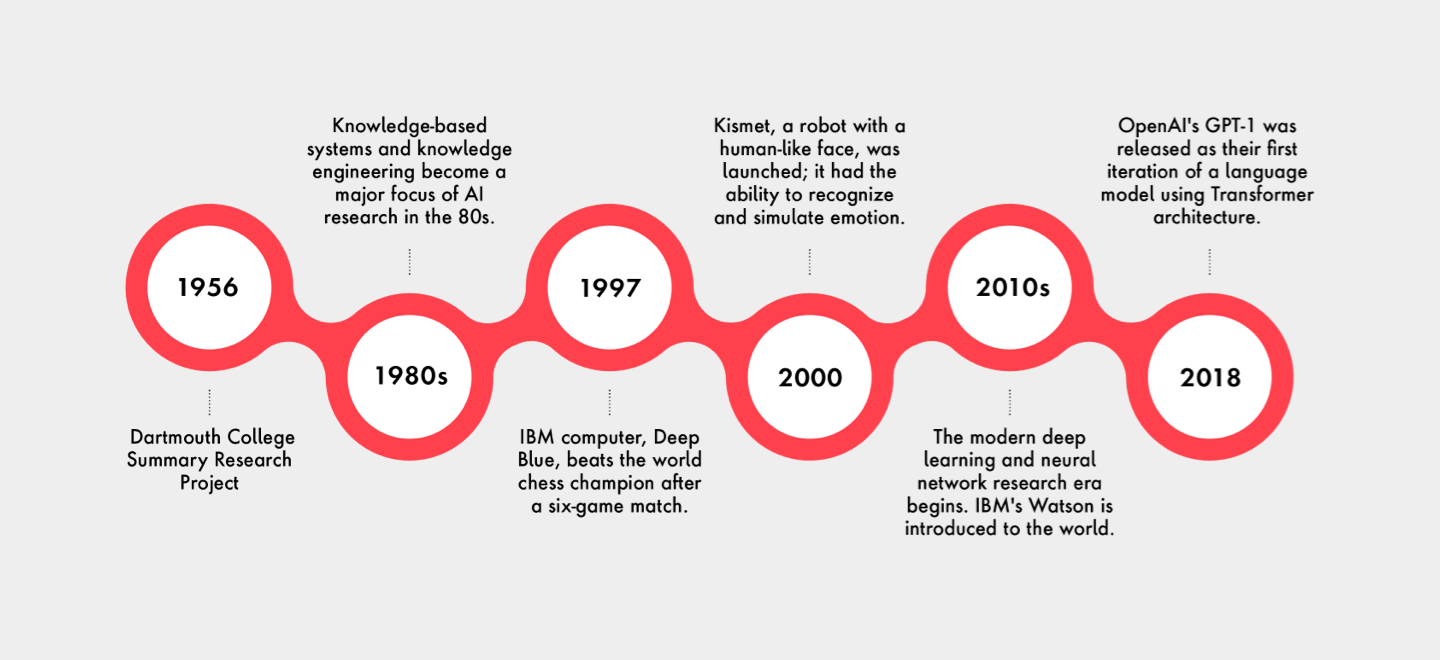
There are two driving forces that have contributed to the breakthrough in generative AI. First are the breakthroughs made in the field of artificial intelligence research which began at the Dartmouth College Summary Research Project in 1956. From there, there was further development, from expert systems in the 1970s and 1980s to IBM's Deep Blue chess program in the 1990s to reinforcement learning in the 2000s and the resurgence of neural network research in the 2010s—all of which culminated in the launch of OpenAI's GPT models in 2018 which set new benchmarks in natural language processing and generation.
The second factor is the reduction of compute costs, which have made high-performance computing resources more affordable and available. This has sped up the progress of researchers and developers in their experimentation.
On November 30, 2022, OpenAI brought the field of artificial intelligence into popular culture by launching ChatGPT, a question-and-answer user interface to their GPT-3 large language model, free to everyone. ChatGPT now has over one billion visitors a month. This decision by OpenAI delivered generative AI into both the boardroom and the living room at the same time.
How does generative AI work: Training, context and data. Lots of data
To understand what generative AI is and how it relates to traditional artificial intelligence, we can use the three letters made famous by ChatGPT to explain it—GPT:
Generative:
Generative relates to the model’s ability to generate outputs. Traditional AI or machine learning models solve one specific problem known at the time of training the model (for example, like when you write prompts in ChatGPT). Generative AI models can solve various problems that they have yet to be exposed to. The outputs can be generated in multiple forms of media, from things like language, audio, video and images.


Pre-trained:
The underlying model has been pre-trained on an enormous amount of data before being given specific tasks. This removes a huge barrier to adoption. Whereas, previously, machine learning models generally took months to source, train and deploy the right data on a particular model, a generative AI model can answer prompts in seconds—and applications can be built in hours to days.
Transformer:
Transformers relate to the structure of a neural network to understand context and dependencies within a sequence of words.

What are the business use cases for generative AI: Seek and deploy
There is no shortage of sources of knowledge when it comes to use case applications for generative AI. In fact, ChatGPT itself has no end of advice for people looking for use cases.
However, this form of advice often fails to consider the nuance of a company’s situation or go beyond a surface-level understanding of the problem it is being asked to solve. The best use cases are frequently conjured from a mix of intimate knowledge of consumers (internal or external), an honest assessment of capabilities and a single-mindedness of what will generate value for the business and its customers.
Without wishing to put ChatGPT out of a job, there are several common areas ripe with use cases for generative AI:
1.Replace onerous processes with a conversational user interface (UI)
- e.g., help consumers fill out complex forms that witness high levels of dropout—mortgage applications or insurance claims
- e.g., streamline colleagues having to log into multiple systems to manage customer service interactions in a contact center
2.Enhance human understanding and productivity
- e.g., the world is full of reports that nobody reads—summarize the findings and share a concise digest with colleagues
- e.g., analyzing the huge amount of unstructured data businesses collect but never making sense of it
3.Automate the boring stuff
- e.g., add intelligence to robotic process automation (RPA) through natural language understanding
- e.g., automate the process of checking marketing assets against brand guidelines to focus resources on items that fail the test and remove the effort on items that clearly pass
There is no shortage of use cases or even methods for generating use cases. The art is ensuring that prioritization is given to those that are viable, feasible and desirable.
What’s next for generative AI: The next move
This wave of interest is led by the versatility of application, the speed/efficiency of development time and the abstract nature of problem-solving. This means that generative AI is more accessible to a wider audience than traditional AI.
Where a complicated machine learning use case may have taken 12-18 months to deploy, the promise of generative AI is to slash that time down to weeks. Building enterprise-grade software is unlikely to be featured in a ‘how-to’ YouTube video but the promise of cheaper, faster deployment is real.
Power is in the people’s hands: Democratizing access
It is rare for a technology to get into the hands of consumers at the same time as big business. The pace of evolution in AI models and startups makes predicting six months into the future, let alone five years, a risky proposition.
However, understanding and making sense of human nature is a more well documented field. Anything that saves people time and/or money is going to popular amongst consumers, particularly in times of economic hardship. Understanding how human behavior will adapt to a world with cheap artificial intelligence at the touch of a button is the key to unlocking where the value resides for a business.
In 2020, recognizing the importance of AI to our future business, we launched PS AI Labs, a dedicated arm of our business focused on promoting, experimenting, and realizing the opportunity presented by AI. With a three-year track record of delivering generative AI solutions, we believe Publicis Sapient is well-placed to partner with our clients on their own generative AI journey.





