What issue can we solve for you?
Type in your prompt above or try one of these suggestions
Suggested Prompt


What is digital business transformation?
Digital business transformation (DBT) is a holistic approach to how organizations think, organize, operate and behave. It enables businesses and institutions to adopt and integrate technology across all facets of the organization. By embedding modern platforms that leverage data and AI, companies become more streamlined and effective, making customers happier and more loyal.
Beyond digitizing parts of a business or adding limited revenue as a stopgap, true digital business transformation helps companies become digital at the core—upgrading legacy systems, reimagining user experience and unlocking value at every touchpoint.
In an increasingly digital world, implementing a data-led transformation strategy is table stakes for organizations to stay relevant amid a constant drumbeat of emerging technologies and skyrocketing customer expectations.
But digital business transformation becomes more complex and more important with the introduction of additional technologies and technology accelerators, like AI. While we at Publicis Sapient have been experts in digital transformation for more than 30 years, DBT continues to evolve, and it is crucial for businesses to evolve with it.
Publicis Sapient has been digitally transforming our clients' businesses for more than 30 years. We've partnered with clients across all industries and helped them stay relevant in the digital age through the launch of the first online banks, travel portals, stock creating platforms, and retail commerce platforms.
Why digital transformation matters in 2024 and beyond
Digitalization has sparked a seismic shift in the way companies connect with customers, align on business goals and approach market challenges on a global scale. So why all the buzz around digital transformation?
In a word: survival.
In today’s world, most organizations have a digital and AI transformation currently underway—and for good reason. With the pace of digital innovation expected to keep accelerating by the nanosecond, falling behind the technology curve is an existential threat to organizations looking to stay relevant in the digital age.
As smarter technologies and disruptive innovation continue to raise the bar on consumer expectations, business environments are in a constant state of flux. Through a pragmatic digital strategy built on modern ways of working, organizations are closing the gap between what consumers expect and what traditional business models can deliver.
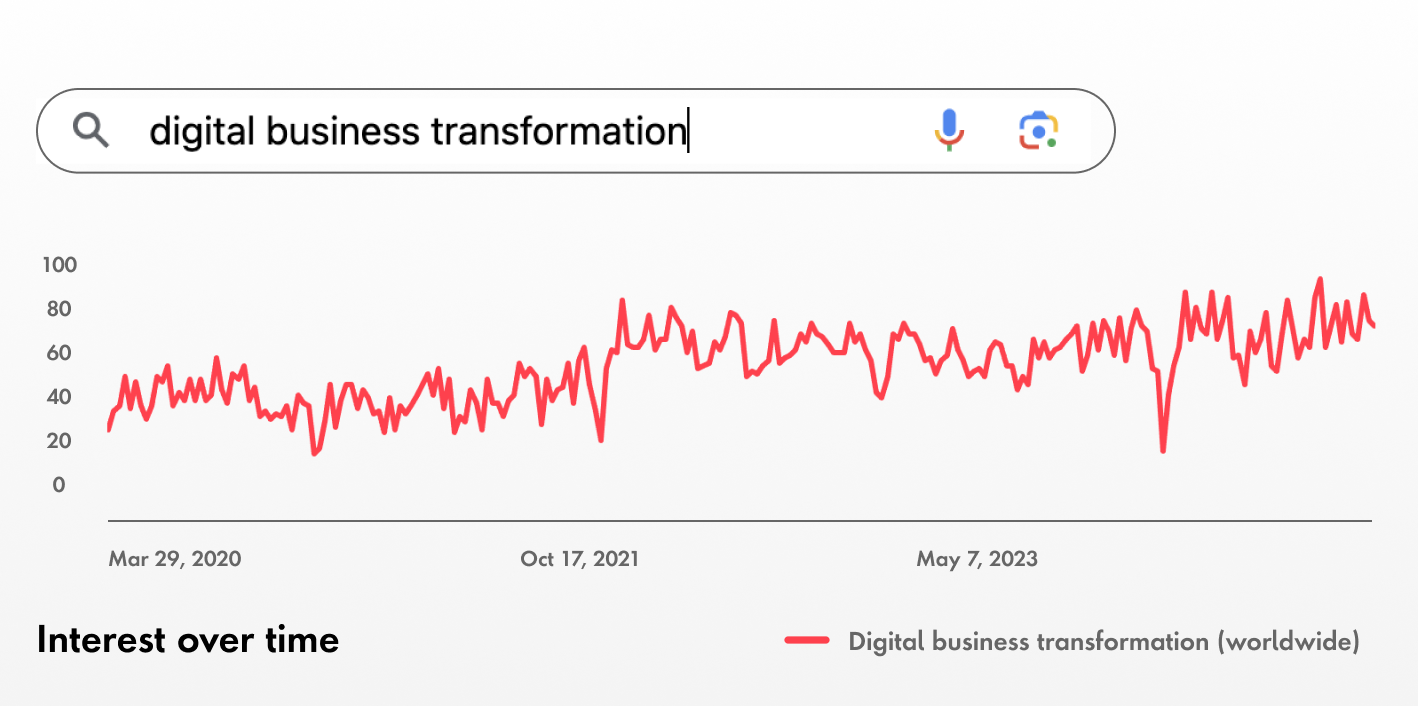
Google search trends show that “digital business transformation” searches have been steadily increasing since COVID-19 and aren’t slowing down.
DBT is also becoming more important for shareholder returns and equity. According to a Harvard Business Review study, from 2018 to 2022, companies recognized as digital leaders saw an average yearly total shareholder return of 8.1 percent, compared to 4.9 percent for those falling behind. Additionally, these leaders experienced a notable increase in return on pretax tangible equity (ROTE), rising from 15.5 percent in 2018 to 19.3 percent by 2022. In contrast, the ROTE for lagging companies grew more modestly, from 13.6 percent to 15.3 percent over the same period.
Change, as they say, is inevitable. But the benefits of a successful digital transformation is impossible to overstate.
By adopting a digital-first, customer-centric mindset built on perpetual innovation, brands can sustain relevance by adapting to change and capturing value through digital—all while driving meaningful impact for their employees, customers and communities.

The core pillars of digital business transformation
New technology, like AI tools, isn’t the only factor forcing businesses to transform.
These are the four main forces of connected change catalyzing companies to accelerate their digital transformation strategy:

Customer behavior: This refers to the evolving expectations and preferences of customers in the digital age. As technology advances, customers demand more personalized, seamless and convenient experiences. Businesses must adapt to these changing behaviors by leveraging digital tools to enhance customer engagement, improve service delivery and create value.
Example: Nearly half of consumers make purchasing decisions through reading product reviews online (41 percent) or using online search to conduct research (45 percent), according to Publicis Sapient research.
Technological change: This encompasses the rapid advancements in technology that are reshaping industries. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and the internet of things (IoT) are enabling new ways of operating and delivering services. Organizations must embrace these technologies to stay competitive, improve efficiency and drive innovation.
Example: More than half of Gen Z (54 percent) uses generative AI tools personally and professionally, according to Publicis Sapient research.
Business models: Digital transformation often requires rethinking traditional business models. This involves leveraging digital technologies to create new revenue streams, optimize operations and enhance customer value. Companies may need to shift from product-centric to service-oriented models or adopt platform-based approaches to remain relevant in a digital-first world.
Example: Forty-three percent of Gen Z and 64 percent of millennials prefer shopping D2C, directly through a brand’s e-commerce website, according to a PYMNTS survey.
See how Sonepar created an omnichannel B2B platform in nine months
Societal change: This refers to the broader shifts in society that impact businesses, such as changes in demographics, cultural norms and regulatory environments. Digital transformation must consider these societal changes to ensure that business strategies are aligned with evolving social expectations and legal requirements. This includes addressing issues like data privacy, sustainability and ethical use of technology.
Example: According to a Pew Research Center survey, 35 percent of workers with jobs that can be done remotely work from home all the time, compared to only 7 percent before the pandemic.

A step-by-step guide to digital business transformation
In order to guide digital business transformation efforts, clarify the expected value or ROI and create a vision for the future, companies must understand their current state and their goal future state.
To do this, companies can use the Digital Transformation Index (DTI). The DTI is a holistic framework to measure the digital maturity of global enterprises and develop a roadmap toward digital excellence.
DTI helps businesses identify areas of relative strength and opportunities for development on their digital transformation journey. It helps create a vision and roadmap for finding untapped potential and unlocking digital transformation opportunities.
“This will allow our clients to develop a data-driven vision,” said Jitender Batra, associate managing director at Publicis Sapient. He added that it will help these businesses with resource allocation.
What are the three pillars of digital transformation?
The DTI framework assesses the current state of digital maturity across three categories and nine sub-categories:
Value creation and exchange
- Digital strategy and innovation: Examines an organization’s ability to craft a clear digital strategy and foster innovation, using technology to reinvent business models and introduce new offerings
- Customer-centricity: Assesses how well a company places customers at the heart of its digital approach, improving experiences, meeting needs and strengthening relationships through technology
- Governance: Evaluates the structures and processes that manage digital transformation, including risk management, data privacy, security and regulatory compliance
Operating model
- Agile ways of working: Measures the organization's ability to implement Agile methodologies for rapid, iterative development essential to thriving in the digital age
- Cross-functional alignment: Focuses on breaking down silos to enable collaboration across teams, driving integrated digital solutions
- Organizational structure: Evaluates whether the company’s structure promotes or obstructs digital growth, emphasizing culture, digital skills and talent retention
Data and technology
- Data availability and use: Reviews how effectively an organization gathers, manages and utilizes data to fuel its digital efforts
- Analytics and measurement: Measures the organization’s capacity to use analytics for tracking progress, making data-driven decisions and gaining insights
- Tech infrastructure and enablers: Looks at how the organization uses technology, such as cloud computing, AI and IoT, to support digital growth
This shows that DBT is not all about the right tools—it heavily relies on these three pillars.
According to Publicis Sapient experts, in most DBT projects, companies either focus on new products (value creation and exchange), back-office technology (data and technology) or pivoting their organizational structure (operating model).
But most are not activating all three pillars of DBT at the same time, and this is where leaders struggle. Where do you start? What do you focus on at different points on the journey? Even the most senior leaders are relying on learning new things, and their playbook doesn’t work anymore.
"Every client is looking for us to tell a really good story about how to change. Even if they are on a transformation journey, it’s so hard. No one has it all figured out."
Alyssa Altman , Transportation and Mobility Industry Lead
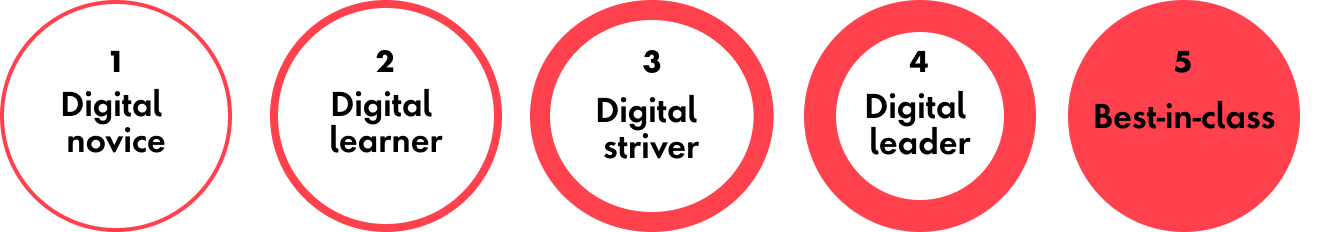
With a consistent and evidence-based methodology, the DTI uses a five-point scale to assess where clients are on their journeys to digital maturity across the organizing framework’s nine dimensions:
In addition to digital maturity, the DTI can be used to optimize multiple functions across an organization:
-
Commercial
- Marketing
- Product design
- After sales
Operations
- Supply chain
- Manufacturing
- Distribution
Back office
- Finance
- Information technology
- Human resources
The DTI works as a first step toward digital maturity or a check-up for businesses with a transformation program underway. This comprehensive process will give you a clear picture of where you stand and what you need to do.
Common digital business transformation obstacles and how to overcome them
While every DBT project is different, there are three key common obstacles that we see companies face over and over again: organizational change resistance, legacy systems and processes and a cultural shift.
Organizational change resistance
One of the primary challenges is the resistance to change within an organization. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding or fear of the unknown, making it difficult to effectively implement new digital strategies.
Example: Kodak is a classic example of a company that faced significant resistance to change. Despite inventing the first digital camera, Kodak was slow to embrace digital photography due to internal resistance and a strong attachment to its traditional film business. This resistance to change ultimately led to Kodak's decline as digital photography became the norm.


Legacy systems and processes
Many established companies struggle with outdated legacy systems and processes that are not conducive to digital transformation. These systems can be costly and complex to update or replace, posing a significant barrier to the adoption of new technologies.
Example: Sears struggled with outdated legacy systems that hindered its ability to compete in the digital retail space. The company's reliance on old technology and processes made it difficult to implement modern e-commerce solutions and adapt to changing consumer behaviors. This inability to update its systems and processes contributed to Sears' decline in the face of more agile and digitally savvy competitors.
Cultural shift
Digital transformation requires a cultural shift within the organization. While this might sound similar to organizational change resistance, this is less about fear of the unknown and unwillingness to change and more about creating a space to be innovative. This involves changing the mindset of employees and leadership to embrace innovation, agility and a customer-centric approach. Achieving this cultural change can be challenging, as it often requires redefining roles, responsibilities and company values.
Example: Blockbuster's failure to adapt to the digital age is often attributed to its inability to shift its corporate culture. The company was slow to recognize the potential of digital streaming and clung to its traditional rental model. This cultural inertia allowed competitors like Netflix to capture the market by embracing digital innovation and customer-centric approaches.

Emerging Trends Driving Digital Transformation
Emerging Trends Driving Digital Transformation
Real-World Success Stories in Digital Transformation
Digital business transformation case studies can take many forms, as DBT projects are not one-size-fits all.
Often DBT work starts with a simple request, like “We need a new e-commerce website,” but the project morphs into something entirely different to address the root problem. This could be a customer journey that flows in parallel to an employee journey, which requires upgrading legacy applications, or potentially breaking down silos between brands or functional teams to increase efficiency and data sharing.
These are a few examples of how DBT has come to life at global enterprises, in different ways:
-
![]()
Nissan
The project: Publicis Sapient utilized artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to help Nissan improve their test drive conversion rates. They consolidated data assets from 190 markets onto a single platform to better understand digital customers at scale. Results: This transformation led to a 900% increase in test drives, showcasing the power of data-driven insights and personalized customer engagement.
-
![]()
Marriott
The project: Publicis Sapient assisted Marriott in creating a global home rental platform to offer a new type of travel accommodation for their hotel guests. This initiative was part of Marriott's strategy to enhance their digital presence and provide more personalized experiences. Results: The platform led to a 100% increase in YoY bookings, and enabled Marriott to expand its offerings and compete in the growing home rental market, thereby driving growth and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
![]()
Carrefour
The project: Publicis Sapient partnered with Carrefour to transform the future of digital retail by building an approach that prioritizes shoppers. This involved enhancing the digital retail experience to improve speed and scale, allowing Carrefour to better meet the needs of their customers. Results: The collaboration resulted in 1.5x more conversions and significant improvements in operational efficiency and customer experience, positioning Carrefour as a leader in digital retail transformation.
-
![]()
Sonepar
The project: Publicis Sapient worked with Sonepar to re-energize the B2B buying experience by driving digital transformation and innovation within the company. This involved modernizing their digital platforms to enhance customer engagement and streamline operations. Results: This accelerated nine-month transformation integrated six different operating companies, and led to improved customer experiences and operational efficiencies, helping Sonepar to better serve their clients and stay competitive in the market.

Essential Tools for a Successful Digital Transformation
Many tools necessary for digital business transformation that were once quite innovative, have now become table stakes. This ups the ante for digital business transformation – as it becomes more about enhancing digital technology, rather than just simply building from the ground up.
For example, cloud computing platforms, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide scalable and flexible infrastructure that allows businesses to store and process data efficiently.
According to Publicis Sapient research, out of 1,000 global executives surveyed, 100% reported at least initial cloud adoption and basic implementation, and 50% have advanced cloud services adoption with ongoing optimization, and/or comprehensive cloud integration with a focus on innovation.
The same is true for other essential DBT tools and platforms, such as customer relationship management systems (CRMs), enterprise resource planning systems (ERPs), and data and analytics intelligence tools like Power BI and Google Analytics.
The obstacles don’t necessarily occur when it comes to implementation, but Moreso when it comes to adoption, scaling and systems integration. According to research cited by the Harvard Business review, 87.5% of digital transformations fail.
The numbers are similar when it comes to AI transformation: 89% of large companies globally have a digital and AI transformation underway, but they have only captured 31% of the expected revenue lift and 25% of expected cost savings from the effort.
Now with the acceleration of AI into the enterprise, organizations have the opportunity to integrate AI into various tools and platforms – like CRMs, e-commerce platforms and more – but this requires an even higher level of digital maturity, and is often more complex.
What’s Next for Digital Business Transformation?
The next evolution of digital business transformation is AI transformation.
AI transformation goes beyond digital business transformation; it redefines how businesses operate by leveraging AI as a central component of strategy, operations, and value delivery. Traditional digital transformations focused on integrating technologies like cloud computing or big data analytics to optimize existing operations. AI transformation requires businesses to reimagine their core strategies for problem-solving and innovation using AI, not just to integrate new technologies but to also drive growth and efficiency overall.
With AI transformation, AI becomes not just a tool but a true partner in the business, augmenting human capabilities and providing insights that drive strategic choices.
AI transformation vs. traditional DBT
Traditional DBT focuses on integrating technology to support existing operations, often streamlining workflows or enhancing customer engagement. While DBT often enhances efficiency within existing paradigms, AI Transformation creates entirely new ways of working in partnership with AI that are faster, smarter, and more aligned with the rapid pace of technological change.
For example, in traditional DBT, a retail company might adopt a new operating model to take advantage of new technology, like marketing personalization. In an AI Transformation, that same company would partner with AI tools to create the operating model, make decisions, implement the operating model, and execute the new technology, leading to an entirely new solution and way of thinking.
Digital Business Transformation: The Path to Future-Proofing Your Business
In order to ensure a successful DBT journey, companies need to leverage AI into every aspect of their business – which may mean completely changing ways of working, and continuing to evolve again and again.
Nigel Vaz, CEO of Publicis Sapient, emphasizes the importance of adaptability and continuous learning in futureproofing businesses. He suggests that businesses and their employees must "learn quickly, unlearn and learn again" to remain relevant in a rapidly changing world. This mindset is crucial for businesses to adapt to new market conditions, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations.

What makes our approach to digital transformation unique
At Publicis Sapient we believe the path to successful transformation is paved with continuous innovation and true partnership—the kind that works with you every step of the way from ideation to implementation to get to where you want to go. And it all starts with a simple idea: putting people first.
Our capabilities and unique SPEED approach to scalable digitalization are grounded in a dual view of both our clients and their customers—a people-centric lens that sharpens the way we consult, strategize and solve problems.
We often say that transformation is a journey that transcends the destination—fusing Strategy, Product, Experience, Engineering, Data and AI (SPEED) to accelerate growth and create a foundation for perpetual change: getting smarter and more hyper automated at every stage. Because digital business transformation is a never-ending journey, guidance from a trusted transformation partner to provide support becomes even more important.
At Publicis Sapient, we work side-by-side with our clients to ensure their bold visions become a reality. Our comprehensive Sapient AI solutions, leveraging proprietary AI tools like Sapient Slingshot and Bodhi and an AI-assisted agile approach, automate complex processes and elevate your organization’s potential. Wherever you are on your transformation journey, AI will shape your future—and we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Recognized as a 2023 Market Leader in Generative Enterprise Services by HFS Research, our teams have experience designing and building innovative AI solutions. By integrating a holistic approach to how organizations think, organize, operate and behave, and by blending customer centricity with best-in-class strategy and engineering, we’ve helped organizations radically transform for more than 30 years.
Related Reading
-
![]()
About Us
About Us
We don’t just help your business adapt to change. We make you really good at it. Get to know the company that’s been partnering with Fortune 500 businesses for over 30 years, to build their competitive advantage through digital.
-
![]()
Sapient AI Solutions
Transform your business with tailored AI strategies designed to unlock unique value and drive digital innovation sustainably.
-
![]()
What is SPEED?
Discover Publicis Sapient's unique SPEED capabilities—strategy, product, experience, engineering, and data & AI—driving digital business transformations at scale.












