What issue can we solve for you?
Type in your prompt above or try one of these suggestions
Suggested Prompt


In the News
Why Swap Trade Confirmations Could Benefit from RPA
The over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives post-trade processing and market infrastructure landscape has changed considerably since the first executed interest rate swap in 1981. However, despite some advances, the swap trade confirmation process still requires significant human intervention, highlighting the need for automation—and more specifically, robotic process automation (RPA).
Industry advances have positively affected the timeliness of confirmation processing and mitigated operational risk. For one, short-form confirmations have mostly replaced long-form paper confirmation, reducing the number of fields firms need to exchange and match. For another, the development of industry solutions that leverage industry standard International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) documentation now facilitate the electronic exchange and matching of trade details.
Yet in spite of the above industry developments, the swap trade confirmation process relies on time-consuming human intervention mainly due to the following reasons:
- Customized confirmation templates that differ among counterparties
- Lifecycle event management that leads to additional complexities such as cash settlements, partial unwinds and trade novations
- Operational errors in trade capture especially for non-electronic and non-standardized trades
- Managing nuances of individual asset classes
- Increased regulatory reporting requirements such as MIFID II
Human intervention is not only operationally time consuming but also costly. It requires significant manpower to manage the trade confirmations on a day-to-day basis. Further, scaling trade volumes provides additional challenges in terms of controlling cost and resources.
Bring on the robots
RPA provides the opportunity to implement intelligent automation solutions to minimize the time and cost associated with swap trade confirmations.
In simple terms, RPA is a software that helps automate any repetitive, rules-based and high-volume process that either requires human effort or is susceptible to human error and miscalculation. A software “robot” is used to capture the steps required to complete a process that may involve interacting with an application. The software works with the application in the same way a human does.
To fully appreciate the range of challenges related to swap trade confirmations, we should start by looking at the generic swap trade confirmation process flow, as depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1:
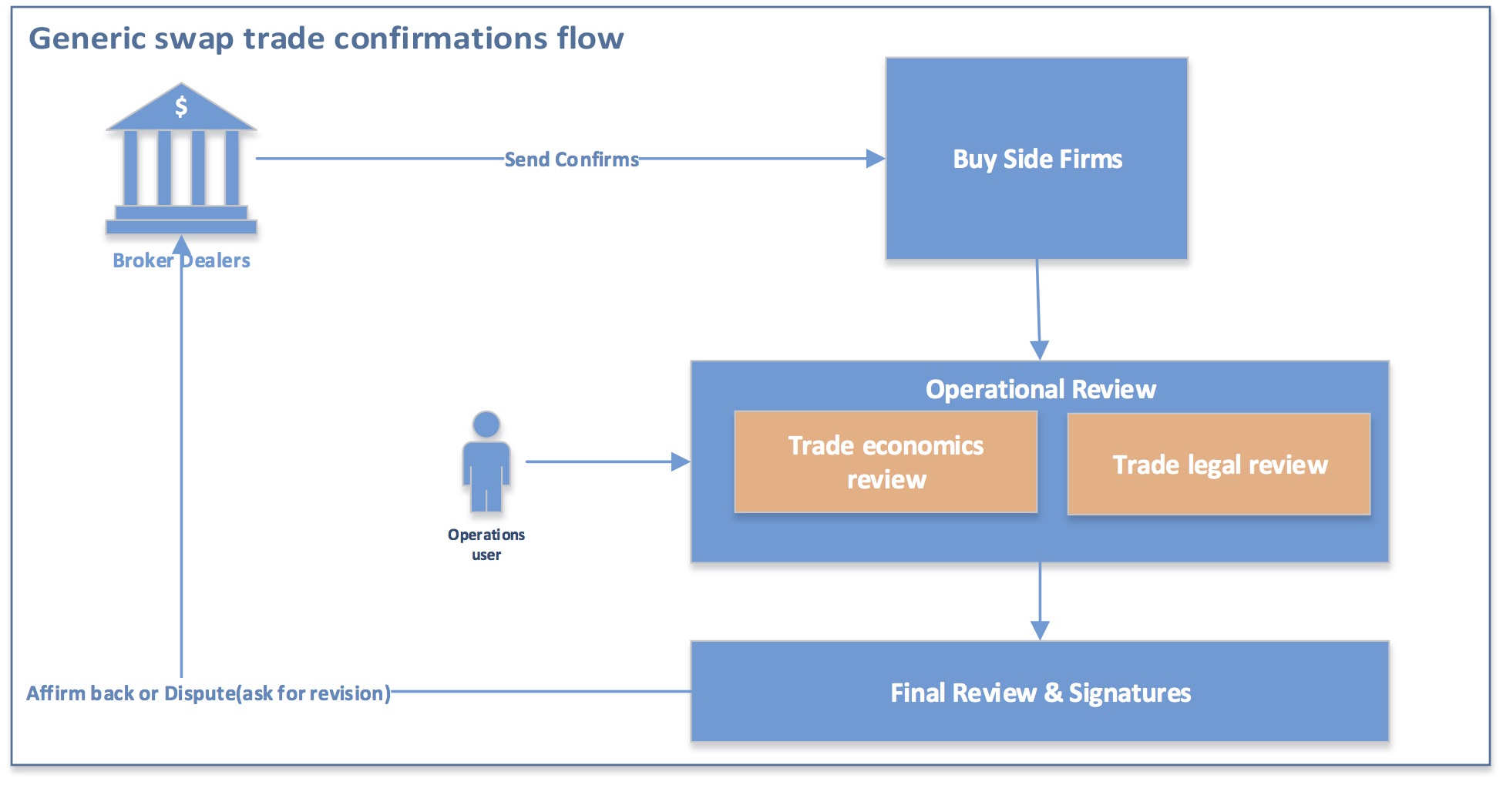
At a glance, the above process flow might look very simple. In reality, it is very complex. In the operational review, buy-side firms spend considerable time and manpower to ensure all key trade terms are accurately captured. The operational review is further complicated when broker-dealers have different confirmation templates. As a result, the operational users spend more time dealing with varied formats.
Another challenge lies in the nuances of different asset classes. For example, terms that need to be matched for an interest swap contract differ from an equity swap contract. The operational knowledge of such products is vital to efficiently manage the trade confirmation process.
Finally, timelines are extended with trade disputes. Generally, in the case of a trade dispute, firms ask broker-dealers to send revised confirmations after correcting the trade terms. In this scenario, firms have to engage in a second operational review of revised paper confirmations.
The RPA solution
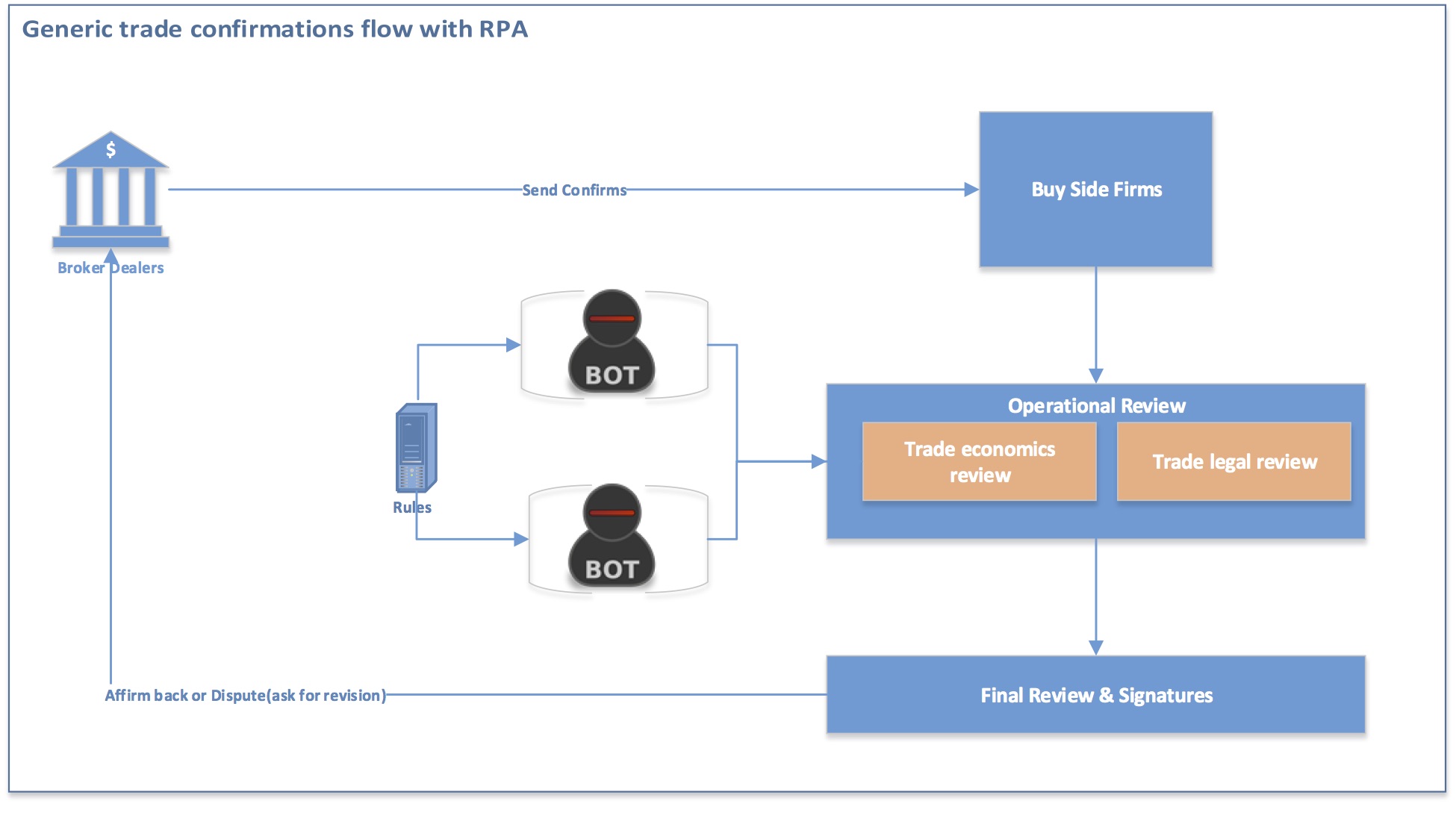
To extend RPA to the swap trade confirmation process, firms should create a rules-based framework that allows users (using RPA tools) to configure business rules to extract and link counterparty trade data with the firm trade data. Automated bots are deployed that mimic human actions to look-up and reconcile the key trade attributes to arrive at a match.
The logical architecture usually entails three key components:
- Centralized configuration of rules—Enables a “create once, use by many” paradigm and also eases the operational maintenance of rules on an ongoing basis
- BOTs—Mimics the user workspace so they can run the process just like humans by using configured rules. The number of BOTs can vary depending upon the operational need. It’s akin to adding more people to the process
- Monitoring—Usually involves specific alerts to avoid process interruptions due to infrastructure and environment issues
Figure 2: The swap trade confirmation process with an RPA implementation
However, extending RPA to the swap trade confirmation process should not be an all or none proposition. The process itself is complex and has many exception paths, including extracting trade data from different counterparty templates, navigating third-party applications and handling mismatches and disputes. The approach should be incremental in nature, automating the use cases that are less complex but high in value first, and then gradually moving up the value chain.
Below is a six-step approach for such an implementation:
- Process Analysis—The first step in the RPA implementation entails a detailed process analysis. This is where the process in its current form should be documented and outlined in detail. The different interfaces and touchpoints should be determined and each distinct process path should be listed clearly.
- Process Prioritization—This step involves prioritizing each listed use case. At a minimum, every use case should be labelled by its level of complexity and value. For example, a use case can be labelled low in complexity if there are minimum touchpoints and the rules can be objectively defined. Process prioritization is important as it clearly lays out what should be the starting point for automation.
- Process Re-engineering—Should be thought in terms of how a current process needs to be tweaked for efficiencies in order for automated bots to perform the same process with minimum interruptions and exceptions. For example, a process may need a defined checklist for the bots to complete the tasks and remove any inherent subjectivity.
- Process Implementation—Where the actual RPA implementation takes place. Specific business rules are configured within RPA tools to be utilized by the bots to run the process in an automated way. It’s similar to outlining process instructions for bots. Instead it’s in a sequential and rules-based manner.
- Process Validation—The last step from an implementation standpoint. It entails testing the different touchpoints and interfaces, including validating the configured rules and running the automated bots to perform a process in a simulated environment.
- Process Monitoring—An ongoing step of monitoring processes and bots for interruptions, failures and overall performance. It’s a feedback loop of the previous five steps that provides real-time information about any deficiencies, paving the way for an incremental approach to implementation.
RPA for swap trade confirmation provides a perfect opportunity to automate the operational review of trades. Bots can use a rules-based framework to automatically link trades, match key trade terms and approve the trade for a next level review. The automation of these operational steps could result in significant efficiency gains and improve scalability while minimizing costs and manual effort. And by switching to a rules-based automated operational review, companies can better manage operational risk.






